Registry¶
A Registry document allows users to write, cancel and modify items of a datamart. Knowage allows users to implement a Registry document through the Qbe Engine. By the way it has a different graphical interface compared to the Qbe one. An example is given in the following figure. In next chapters we will see how to navigate a Registry document (Registry features paragraph) and how to create a new one (Registry development paragraph).
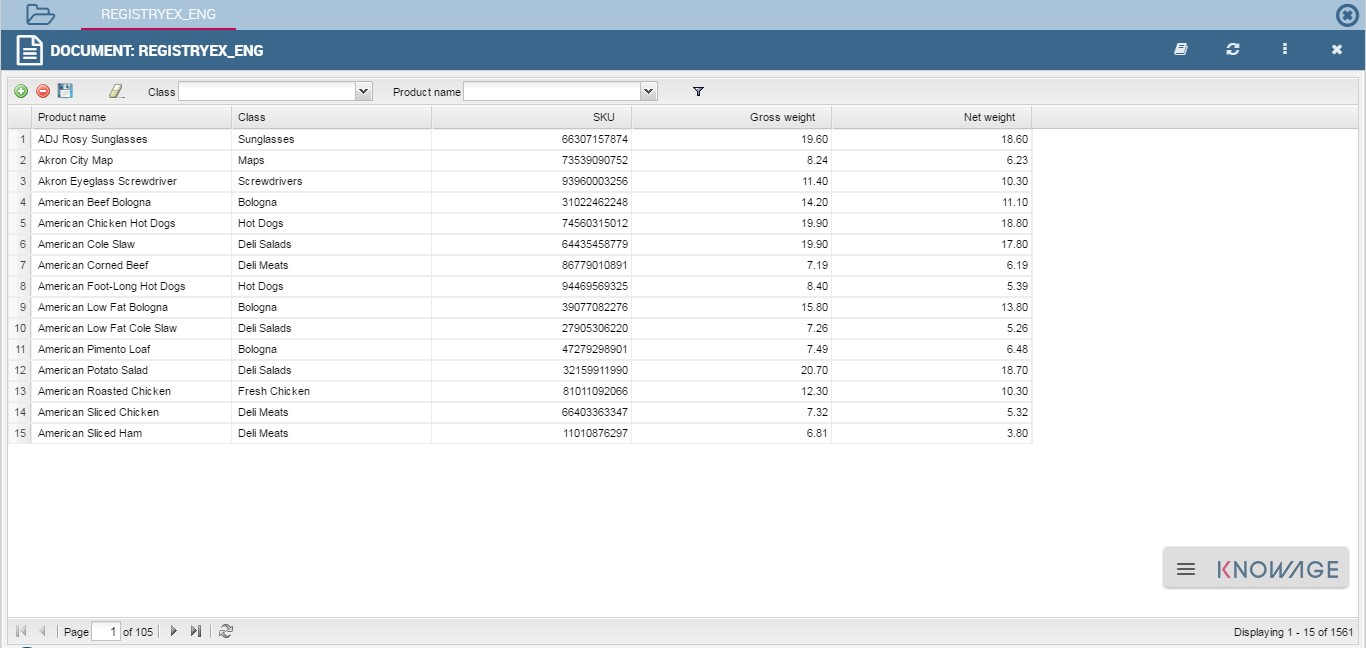
Fig. 352 Example of Registry document.
Registry features¶
The execution of a Registry document opens a plain table: the records are shown in rows and they can be browsed using the pagination available at the bottom of the window. We underline that it is possible to edit each item of the table. Just double-click on a cell you may wish to rearrange and type a string or a numeric value accordingly. Some examples are highlighted below.
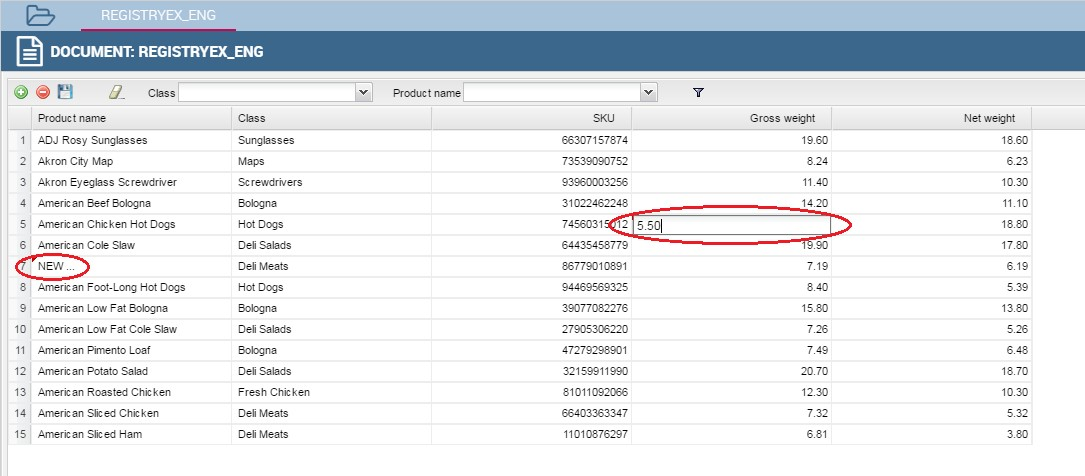
Fig. 353 Editing table cells.
Moreover, you can add new rows from scratch selecting the “Plus” icon  on the left of the functionality bar (see next figure) available at the top of the window. Insert in each cell the corresponding value: string or number.
on the left of the functionality bar (see next figure) available at the top of the window. Insert in each cell the corresponding value: string or number.

Fig. 354 Functionality bar.
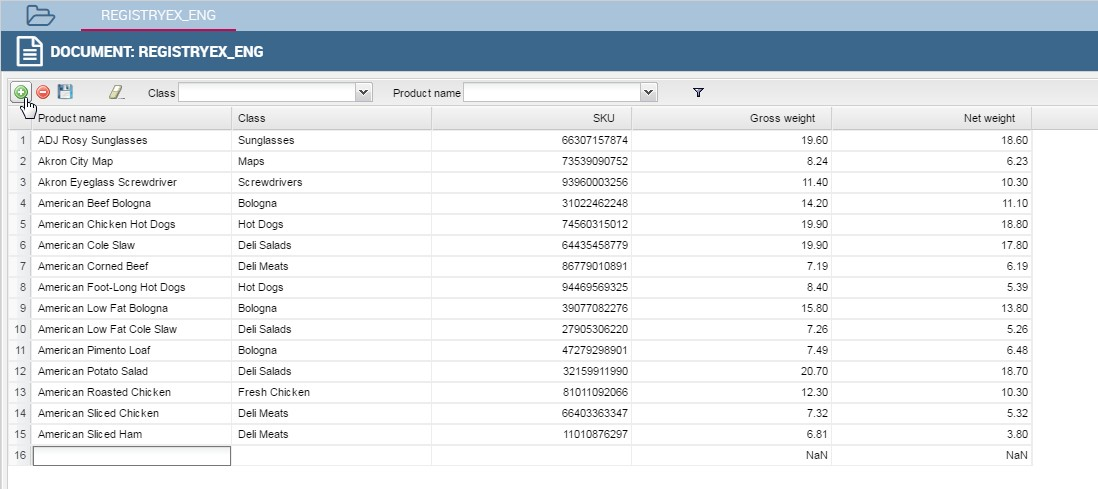
Fig. 355 Adding a new row.
Vice versa, you can delete one or more rows using the “Minus” icon  of the functionality bar (Fig. 354) available at the top of the window.
of the functionality bar (Fig. 354) available at the top of the window.
It is important to click on the Save button  to store the adjustments done in the datamart.
to store the adjustments done in the datamart.
Furthermore you can use filters, if implemented, of the functionality bar. Pick one field out of the combobox. Click on the “Filter” icon  to run the functionality. Otherwise, click on the “Cancel” icon
to run the functionality. Otherwise, click on the “Cancel” icon  to clear the boxes off.
to clear the boxes off.
Note that, since records are displayed in a plain table, it is available a combobox (see figure below) which allows the user to visualize all fields related to the record of the previous cell and then change from one to another to get all data.
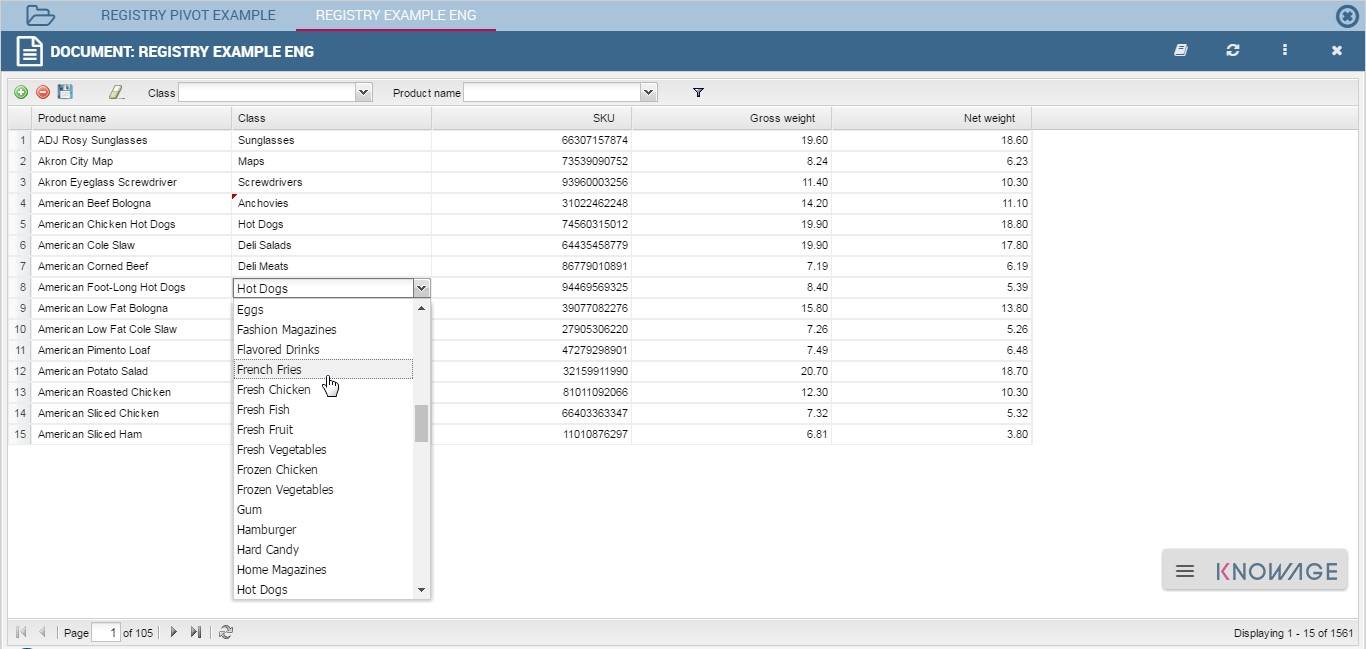
Fig. 356 Select one field from a combobox.
JPivot Registry characteristics¶
It is possible to implement also a JPivot Registry document. The graphical features are very similar to the ones exposed in Registry development paragraph. An example is given below.
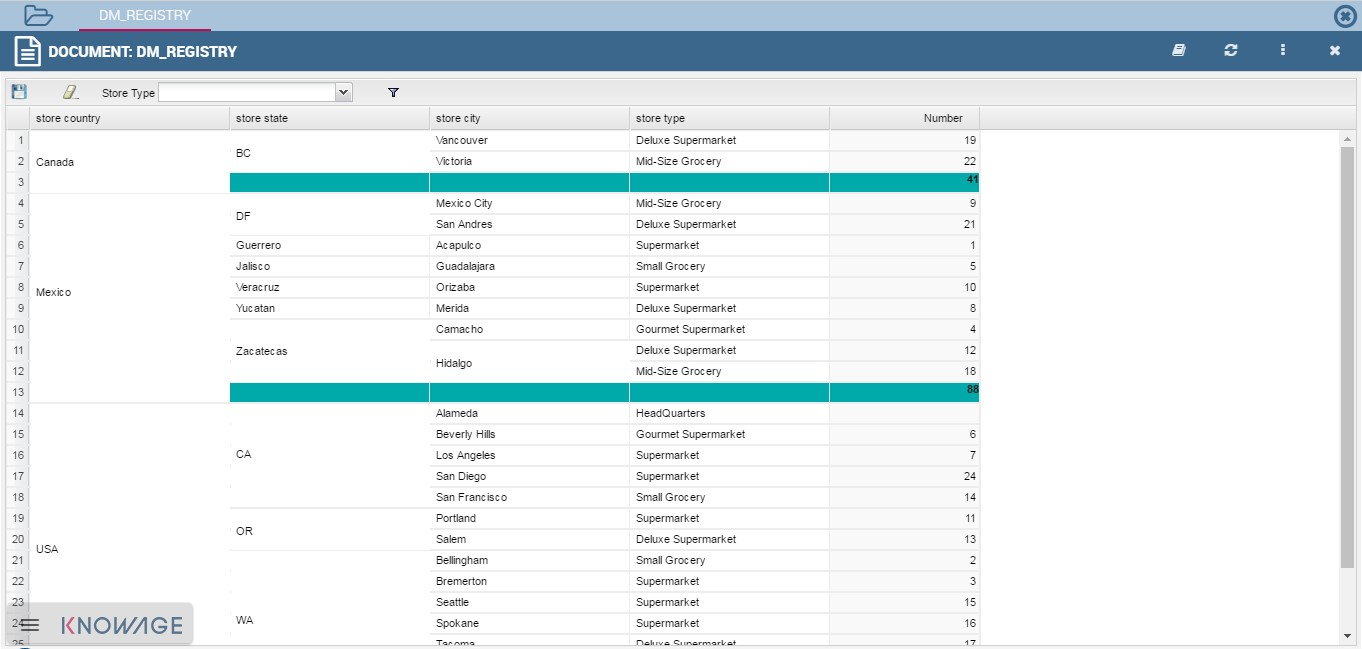
Fig. 357 Example of Jpivot Registry document.
In this case the table shows columns organized in a hierarchical way and a grouping function is implemented. From the left to the right the columns contain fields at different detail levels. The last column in our example in the figure above contains numeric data. Such a field is grouped at the “country” level. The grouping level depends on the configurations made on template building.
In the JPivot instance it is not allowed to add, modify or cancel rows. Furthermore, it is not permitted to edit cells which contain string items while the numeric ones are still changeable. If implemented filters are still available.
Registry development¶
To create a Registry document there must be available a datamart schema on Knowage Server. Then you must edit an XML template. The latter is very similar to the one produced under the Qbe development but in this case you must add an appropriate tag. Indeed, if the template file has the <REGISTRY> tag the engine shows data in registry modality; namely it shows a table whose rows are manageable by end users by adding, editing or deleting them.
Here we exhibit a possible syntax for a Registry document.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1250"?>
<QBE>
<DATAMART name="RegFoodmartModel" />
<REGISTRY>
<ENTITY name="it.eng.spagobi.meta.Product">
<FILTERS>
<FILTER title="Class" field="product_subcategory" presentation="COMBO" />
<FILTER title= "Product name" field="product_name" presentation="COMBO" />
</FILTERS>
<COLUMNS>
<COLUMN field="product_id" unsigned="true" visible="false" editable="false" format="####" />
<COLUMN field="product_name" title="Product name" size="200"
editor= "MANUAL" sorter="ASC"/>
<COLUMN field="product_subcategory" title="Class" size="200"
subEntity="rel_product_class_id_in_product_class" foreignKey="rel_product_class_id_in_product_class" />
<COLUMN field="SKU" title="SKU" size="200" editor="MANUAL" />
<COLUMN field="gross_weight" title="Gross weight" size="200" editor="MANUAL" />
<COLUMN field="net_weight" title="Net weight" size="200" editor="MANUAL" />
</COLUMNS>
<CONFIGURATIONS>
<CONFIGURATION name="enableButtons" value="true"/>
<CONFIGURATION name="isPkAutoLoad" value="true"/>
</CONFIGURATIONS>
</ENTITY>
</REGISTRY>
</QBE>
|
In particular, we give some details for each tag and main attributes.
- ENTITY: the entity name as in the model;
- FILTERS: possibility to define filters by specifing the title, the field (among shown columns) and the type among COMBO, MANUAL or DRIVER: in this last case user has also to specify the analytical driver that take this filter’s value;
- COLUMNS: columns list specifing:
- field name: the reference to the field identifier into the model,
- title: the title of the column shown (optional),
- visible: the visibility of the column (Optional, default true),
- editable: the editability of the column (Optional, default true),
- color and format for numbers: optional,
- editor: the editor. Default type is free-text for simple column (not fk values), but for date is possible show the picker through the type PICKER. The format option specify the format date,
- subEntity: If the column is a reference key user can specify the subentity referred and the foreign key name; in this case the field shown will be of the entity referred and will be shown as combo if editable,
- dependsFrom: if the column content is logically correlatd to other registry’s column is possible specifiy this logic through this parameter. DependsFrom identifies the field name on which it depends (Optional),
- dependsFromEntity: usable only with dependsFrom parameter. It defines a different entity to resolve the correlation (Optional),
- orderBy: is used in case of foreign key, the combo box is ordered by the column here indicated, by default is the column extracted (Optional).
- infoColumn: if true ignore the column when inserting or updating the record (Optional).
We stress that it is mandatory to point at one datamart table using a column with a numeric key. The code line is highlighted in figure below. While, if not elsewhere specified, a descriptive column will be displayed by default.
1 2 | <COLUMNS>
<COLUMN field="store_id" visible="false" editable="false" />
|
Still referring to the code above, we underline that the “product_subcategory” field is used as a subcategory. It belongs in fact to another table. In this case it is enough to add the attributes: subEntity=”rel_product_class_id_in_product_class” foreignKey=”rel_product_class_id_in_product_class”.
JPivot Registry instance¶
The Registry instance allows to develop also a Jpivot table. See the last figure (above) to have an idea while the syntax example is given in the next code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | <QBE>
<DATAMART name="foodmart" />
<REGISTRY pagination = "false" summaryColor="#00AAAA">
<ENTITY name="it.eng.spagobi.meta.Store">
<FILTERS>
<FILTER title="Store Type" field="store_type" presentation="COMBO" />
</FILTERS>
<COLUMNS>
<COLUMN field="store_id" visible="false" editable ="false" />
<COLUMN field="store_country" title="store country" visible="true"
type="merge" editable ="false" sorter ="ASC" summaryFunction="sum" />
<COLUMN field="store_state" title="store state" visible="true"
type=" merge" editable ="false" sorter ="ASC" />
<COLUMN field="store_city" title="store city" visible="true"
type="merge" editable ="false" sorter ="ASC" />
<COLUMN field="store_type" title="store type" type="merge" sorter="ASC" />
<COLUMN field="store_number" title="Number" size="150"
editable="true" format="########" color="#f9f9f8" type="measure"/>
</COLUMNS>
<CONFIGURATIONS>
<CONFIGURATION name="enableButtons" value="false"/>
</CONFIGURATIONS>
</ENTITY>
</REGISTRY>
</QBE>
|
Note that to activate the JPivot modality it is important to add the attribute type=”merge” and have at least one numeric field. Furthermore the selected column fields must be hierarchically structured.