Advanced configuration¶
In this chapter we will describe all the advanced configuration parameters of Knowage.
Thread manager¶
For Tomcat: the configuration of the pool of thread is available inside the TOMCAT_HOME/conf/server.xml. Refer to Code below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <Resource auth="Container" factory="de.myfoo.commonj.work.FooWorkManagerFactory"
maxThreads="5"
minThreads="1"
queueLength="10"
maxDaemons="10"
name="wm/SpagoWorkManager"
type="commonj.work.WorkManager"/>
|
For JBoss: the configuration of the pool of thread is available inside the JBOSS_HOME/ standalone/configuration/s Refer to Code below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | <object-factory name="java:global/SpagoWorkManager" module="de.myfoo.commonj"
class="de.myfoo.commonj.work.MyFooWorkManagerFactory">
<environment>
<property name="maxThreads" value="5"/>
<property name="minThreads" value="1"/>
<property name="queueLength" value="10"/>
<property name="maxDaemons" value="10"/>
</environment>
</object-factory>
|
In both cases, the meaning of the configuration parameters is the following:
- minThreads: the mininum number of threads in the thread pool. Default: 2;
- maxThreads: the maximum number of threads in the thread pool. Default: 10;
- queueLenght: the number of work items that can be queued - 0 means no queuing. Default: 10;
- maxDaemons: the maximum number of daemon threads to allow for this work manager. Default: 10.
Cache parameters¶
First of all, the user must configure the distributed cache. This helps to coordinate the parallel access to the distributed cache, guaranteeing a thread-safe access. It is necessary to configure the hazelcast.xml file (available in the knowage/WEB-INF/classes/) typing in the ”member“ tag the IP address or hostname of the machine on which Knowage is installed (for example <member> 192.168.29.43</member>). In case of multi-node configuration, it is obviously important to report all cluster members. This operation must be carried out on every node. Furthermore, it is possible to implement a finer tuning of the cache behaviour, changing the Knowage configuration. The user must edit some values of the SBI_CONFIG table using the specific administrator interface.
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.NAMEPREFIX: It configures the prefix of temporary table in the cache ( Default : ”sbicache“ )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.SPACE_AVAILABLE: It resizes cache dimension (bytes) ( Default : 1073741824 )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.LIMIT_FOR_CLEAN: It configures the maximum cache section (in percentage) that can be cleaned at runtime when the cache has not enough space to store a dataset. ( Default : 50)
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.SCHEDULING_FULL_CLEAN: It schedules the recurring operation of complete cleaning of the cache. This periodic cleaning delete all dataset in the cache, without considering further parameters. At the end of the cleaning, the cache is empy. The allowable values are: EVERY_10_MINS, EVERY_15_MINS, EVERY_20_MINS, EVERY_30_MINS, HOURLY,DAILY,WEEKLY,MONTHLY,YEARLY. Every value different from those just listed unenable the periodic cleaning. ( Defualt: DAILY )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.DS_LAST_ACCESS_TTL: It configures the Time To Live of a dataset inside the cache. This parameter defines the minimum TTL (in seconds) so to guarantee that a dataset remains in cache. A too-high value can lead the cache to breakdown (in this case, there is no way to insert new datasets), while a toolow value can lead to situations when there are no certainties of the stability of the dataset in the cache. (Default 600 )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.DATABASE_SCHEMA: Name of the schema on which the tables are created. Such schema is defined by the datasource when it is set as Write-Default. Generally it is not necessary to configure this parameter since it is calculated at runtime. (default <empty> )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.CREATE_AND_PERSIST_TABLE.TIMEOUT: It configures the ratio (in percentage) between the dimension of the cache and the maximum dimension of a dataset in the cache. If the dimension of the dataset which the user intends to persist is bigger than the configured percentage, the system blocks the that persistance attempt. ( Default : 10 )
- SPAGOBI.WORKMANAGER.SQLDBCACHE.TIMEOUT: It represents the maximum waiting time (inmilliseconds) of an asynchronus work. (Default: 180000 )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.HAZELCAST.TIMEOUT : It represents the maximum time (in seconds) to get a distributed lock. ( Default 120 )
- SPAGOBI.CACHE.HAZELCAST.LEASETIME: It represents the maximum time (in seconds) for releasing a distributed lock already got. ( Default :240 )
Logging¶
Knowage uses the component Log4J to create the log applications. Each web application has its own file inside the folder /knowageXXXX/WEB-INF/classes/log4j.properties. The content of this file change accordingly to the settings: the appenders allows to modify the level of the log. As an example, in the following code block, we analize the log file of Knowage. In the first part we can set the generation mechanism of the log file, while ih the second one the level of tracing.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | log4j.rootLogger=ERROR, SpagoBI
# SpagoBI Appender
log4j.appender.SpagoBI=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.File=${catalina.base}/logs/knowage.log
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.MaxFileSize=10000KB
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.MaxBackupIndex=0
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.layout.ConversionPattern=[%t] %d{DATE} %5p %c.%M:%L - %m %n
log4j.appender.SpagoBI.append=false
log4j.appender.Quartz=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.Quartz.File=${catalina.base}/logs/Quartz.log
log4j.appender.Quartz.MaxFileSize=10000KB
log4j.appender.Quartz.MaxBackupIndex=10
log4j.appender.Quartz.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.Quartz.layout.ConversionPattern= [%t] %d{DATE} %5p %c.%M:%L - %m %n
log4j.appender.SpagoBI_Audit=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.SpagoBI_Audit.File=${catalina.base}/logs/knowage_[1]\_OperatorTrace.log
log4j.appender.SpagoBI_Audit.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.SpagoBI_Audit.layout.ConversionPattern=%m%n
log4j.appender.CONSOLE = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.CONSOLE.layout.ConversionPattern=%c.%M: %m%n #
log4j.logger.Spago=ERROR, SpagoBI log4j.additivity.Spago=false
log4j.logger.it.eng.spagobi=ERROR, SpagoBI, CONSOLE
log4j.additivity.it.eng.spagobi=false
log4j.logger.it.eng.spagobi.commons.utilities.messages=ERROR, SpagoBI
log4j.logger.it.eng.spagobi.commons.utilities.urls.WebUrlBuilder=ERROR,SpagoBI
log4j.logger.org.quartz=ERROR, Quartz, CONSOLE
log4j.logger.org.hibernate=ERROR, SpagoBI
log4j.logger.audit=INFO, SpagoBI_Audit log4j.additivity.audit=false
|
If the user wishes to enable the tracing of the information to DEBUG level it is enough to modify the following line
1 | log4j.logger.it.eng.spagobi=ERROR, SpagoBI, CONSOLE
|
in
1 | log4j.logger.it.eng.spagobi=DEBUG, SpagoBI, CONSOLE
|
For further details we refer to the official Log4J documents.
Mail server¶
Knowage uses in some situations the mail server to send emails. The configuration of this feature can be done right straight through the Knowage GUI, after accessing with administrator credentials.
Selecting the category MAIL the user gets the list of parameters to configure for the following profiles:
- trustedStore;
- scheduler, used by the scheduler to send a report by mail;
- user, used directly by the user when he intends to send a report by mail;
- kpi_alarm, used by the alarm component to send mails.
Fig. 3 Mail server configuration.
Moreover, each profile has the following values:
- smtphost: the smpt server,
- Smtpport: the port in use,
- from: the address to which the mail will be associated,
- user: the user of the server connection,
- password: user’s password,
- useSSL: in case the SSl is in use.
Maximum file size¶
For security reasons, Knowage has a series of parameters which manage the maximum file size that can be loaded on the server through the web GUI. To modify those parameters, it is required to enter the Knowage server application as administrator and access the ”server settings“ section and then ”configuration management“. The parameters at issue are the following:
- SPAGOBI.TEMPLATE_MAX_SIZE : TEMPLATE MAX SIZE: it is the maximum template dimension of an anlytical document, expressed in bytes; the default value is 5MB;
- SPAGOBI.DATASET_FILE_MAX_SIZE : DATASET FILE MAX SIZE: it is the maximum dimension of a file used as a dataset, expressed in bytes; the default value is 10MB;
- SPAGOBI.DOCUMENTS.MAX_PREVIEW_IMAGE_SIZE : Max preview image size: it is the maximum dimension of an image used as document preview (in the document browser, for instance), expressed in bytes; the default is 1MB;
- IMAGE_GALLERY.MAX_IMAGE_SIZE_KB : Max image size in Kb:it is the maximum size of the images that can be used in a cockpit creation; the default is 1MB;
Date format¶
Knowage allows the user to visualize the date time in a format that depends on the selected language. To change the visualization of such formats, the user must enter Knowage as administrator and access the “Server Settings“ section and, consequently, the ”Configuration management“. Then finally select ”DATE-FORMAT“.
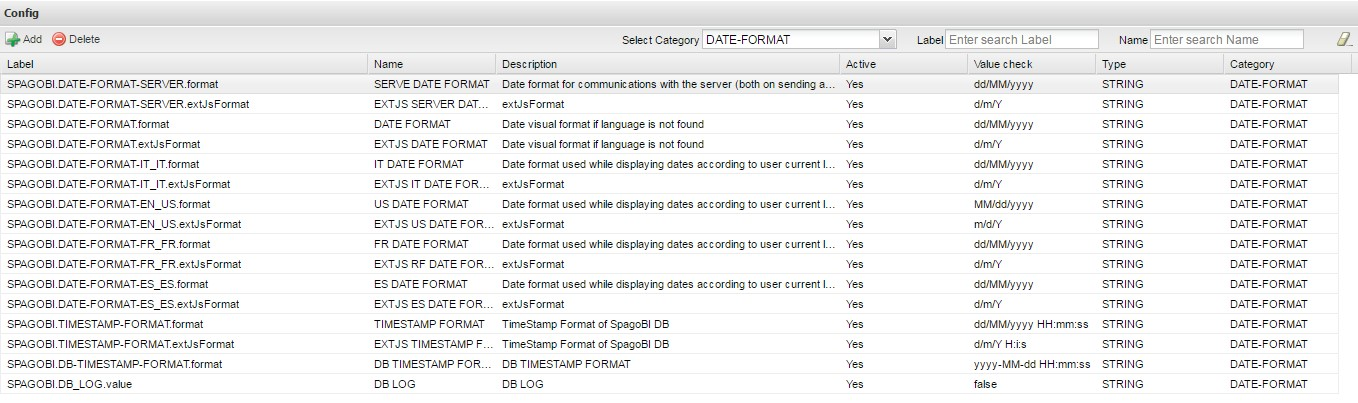
Fig. 4 Date format configuration.
For each available language there are two parameters:
- SPAGOBI.DATE-FORMAT-<lingua>_<nazione>.format: it rules the back-end role;
- SPAGOBI.DATE-FORMAT-<lingua>_<nazione>.extJsFormat: it rules the front-end role.
We suggest to valorize the parameters in compliance with each other, according to a local data.
The parameters SPAGOBI.DATE-FORMAT-SERVER.forma**t and **SPAGOBI.DATE-FORMAT-SERVER.extJsFormat control the link between back-end and front-end. The adjustment of these parameters do not affect the web GUI.
Language¶
Knowage manages the multi-language. The list of all languages is manageable from the “Server Settings” section. Go to “Configuration management“ and select the LANGUAGE_SUPPORTED category. Here there are two properties:
- SPAGOBI.LANGUAGE:sup:`_`SUPPORTED.LANGUAGES :the list of all supported languages underneath this formalism are: [it,IT],[en,US],[fr,FR],[es,ES];
- SPAGOBI.LANGUAGE_SUPPORTED.LANGUAGE.default: the default value is [en,US].
LDAP security connectors¶
Knowage provides integration with a LDAP server for authentication purposes.
Remark. Be sure that the Knowage users have been taken under LDAP census. The LDAP security connectors check the user that is accessing Knowage, but the user must be already defined as a Knowage user. Therefore, the users must cohesist in both authentication systems (LDAP and Knowage).
Knowage ships with two LDAP security connectors:
- LdapSecurityServiceSupplier: a pure LDAP connector that authenticates every user using the LDAP server,
- ProfiledLdapSecurityServiceSupplier: a mixed LDAP connector that can authenticate some users using the LDAP server and other users using the internal Knowage authentication mechanism.
LdapSecurityServiceSupplier relies only on a LDAP configuration file, instead ProfiledLdapSecurityServiceSupplier checks also the Knowage user profile attribute auth_mode.
If the user profile attribute auth_mode is defined and its value equals to internal for the logging user, then Knowage will use its internal authentication mechanism, otherwise it will try an authentication via LDAP.
Warning
The only way to mantain access to Knowage for users not mapped onto LDAP is to:
- define the user profile attribute auth_mode,
- set auth_mode =
internalfor every user not mapped onto LDAP, - use the connector ProfiledLdapSecurityServiceSupplier (see below).
In order to setup any LDAP security connector, prepare a .properties file that includes the LDAP configuration:
- INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY: initial context factory Java class,
- PROVIDER_URL: LDAP server IP,
- SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION: authentication type,
- DN_PREFIX: prefix that will be prepended to the user name to create the DN (distinguished name) of logging user,
- DN_POSTFIX: postfix that will be appended to the user name to create the DN (distinguished name) of logging user;
Important
The final concatenation DN_PREFIX + <Knowage user ID> + DN_POSTFIX must be equal to the DN (distinguished name) of the user as defined in LDAP server. Please check DN examples at https://ldapwiki.com/wiki/DN%20Syntax .
An example of LDAP configuration is the file ldap_authorizations.properties, available in the project knowageldapsecurityprovider.
Then define a custom JVM property ldap.config, setting its value to the path of LDAP configuration file.
In a Unix-like environment using Apache Tomcat you can add a custom JVM property to variable JAVA_OPTS in a setenv.sh file under bin folder:
1 | export JAVA_OPTS="${JAVA_OPTS} -Dldap.config=/opt/tomcat/resources/ldap.properties"
|
In a Windows environment using Apache Tomcat you can add a custom JVM property to variable JAVA_OPTS in a setenv.bat file under bin folder:
1 | set JAVA_OPTS="%JAVA_OPTS% -Dldap.config=C:/Tomcat/resources/ldap.properties"
|
Important
Restart your application server in order to load the custom JVM property.
The final step is to set the LDAP security connector as follow:
- access Knowage as administrator,
- browse to Configuration Management via the main menu,
- set the value of config SPAGOBI.SECURITY.USER-PROFILE-FACTORY-CLASS.className to
it.eng.spagobi.security.LdapSecurityServiceSupplierorit.eng.spagobi.security.ProfiledLdapSecurityServiceSupplier, - save,
- log out of Knowage.
Warning
To recover the default authentication mechanism please revert manually the config SPAGOBI.SECURITY.USER-PROFILE-FACTORY-CLASS.className to its default value it.eng.spagobi.security.InternalSecurityServiceSupplierImpl using a database client.
Knowage is now ready to authenticate the users via LDAP credentials.